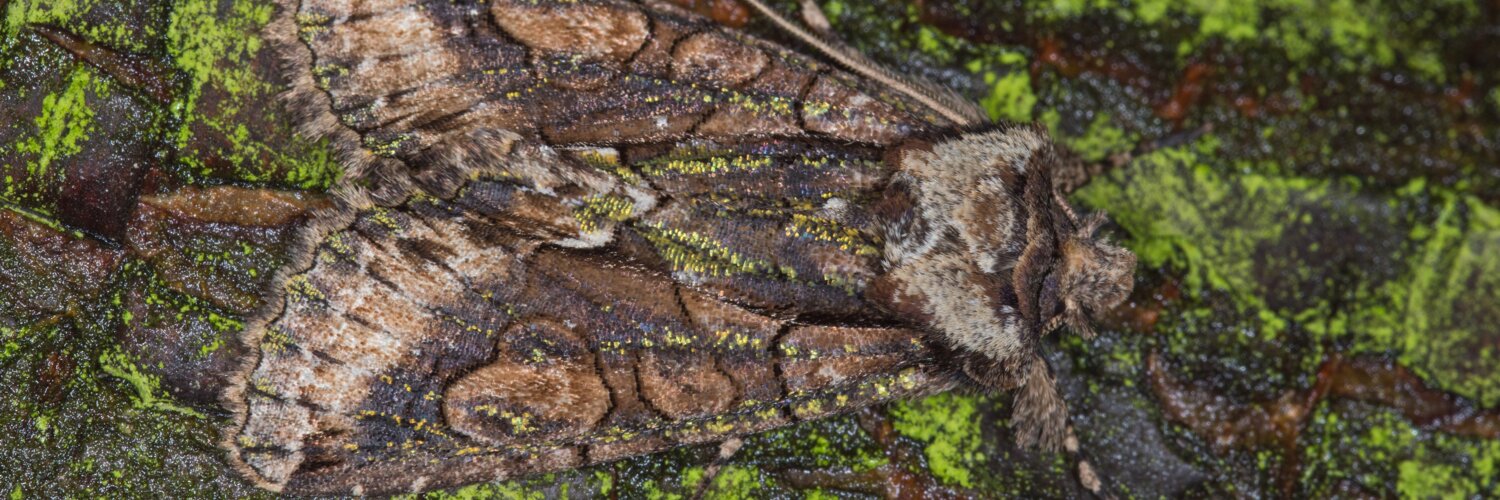
What does camouflage mean?
Effective camouflage involves blurring the distinctive contours of an object to make it nearly indistinguishable from its background. Today, this concept can be applied across various spectral ranges, including the visible spectrum (VIS), near-infrared (NIR), shortwave infrared (SWIR), midwave infrared (MIR), and radar systems.
What is a signature?
An object’s signature is a unique set of data that allows it to be identified. For example, a signature can determine whether a vehicle is conventional or armored and even identify its specific type.
Signatures in the five key spectral ranges (VIS, NIR, SWIR, MIR, and RADAR) are defined by different measurable properties:
- Visible Spectrum (VIS): Focuses on the object’s color and shape.
- Near and Shortwave Infrared (NIR & SWIR): Examines spectral reflectance and shape.
- Thermal Infrared (MIR): Looks at the arrangement and characteristics of warm or hot components.
- Radar Spectrum: Analyzes the spatial and angular distribution of reflected radar signals.
What are spectral ranges?
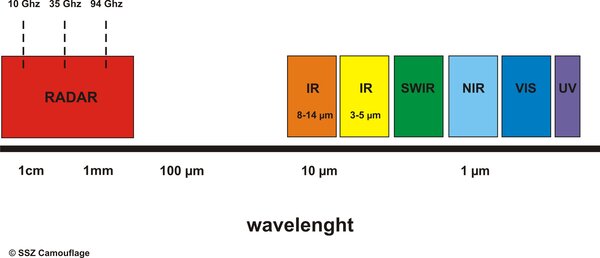
Spectral ranges are parts of the electromagnetic spectrum that can pass through the Earth's atmosphere, known as "atmospheric windows." These include the visible spectrum (VIS), the near-infrared (NIR), the shortwave infrared (SWIR), the thermal infrared ranges at wavelengths of 3-5 µm and 8-12 µm (MIR) and the microwave resp. radar spectrum (RADAR).
Electromagnetic radiation outside these ranges is absorbed by air molecules, making the atmosphere opaque. Among these spectral types, only visible light is detectable by the human eye. All other forms of radiation are invisible.